PgSQL协议分析:网络抓包
Wireshark抓包
Wireshark是一个很有用的工具,特别适合用来分析网络协议。
这里简单介绍使用Wireshark抓包分析PostgreSQL协议的方法。
假设调试本地PostgreSQL实例:127.0.0.1:5432
快速开始
-
下载并安装Wireshark:下载地址
-
选择要抓包的网卡,如果是本地测试选择
lo0即可。 -
添加抓包过滤器,如果PostgreSQL使用默认设置,使用
port 5432即可。 -
开始抓包
-
添加显示过滤器
pgsql,这样就可以滤除无关的TCP协议报文。 -
然后就可以执行一些操作,观察并分析协议了

抓包样例
我们先从最简单的case开始,不使用认证,也不使用SSL,执行以下命令建立一条到PostgreSQL的连接。
psql postgres://localhost:5432/postgres?sslmode=disable -c 'SELECT 1 AS a, 2 AS b;'
注意这里sslmode=disable是不能省略的,不然客户端会默认尝试发送SSL请求。localhost也是不能省略的,不然客户端会默认尝试使用unix socket。
这条Bash命令实际上在PostgreSQL对应着三个协议阶段与5组协议报文
- 启动阶段:客户端建立一条到PostgreSQL服务器的连接。
- 简单查询协议:客户端发送查询命令,服务器回送查询结果。
- 终止:客户端中断连接。
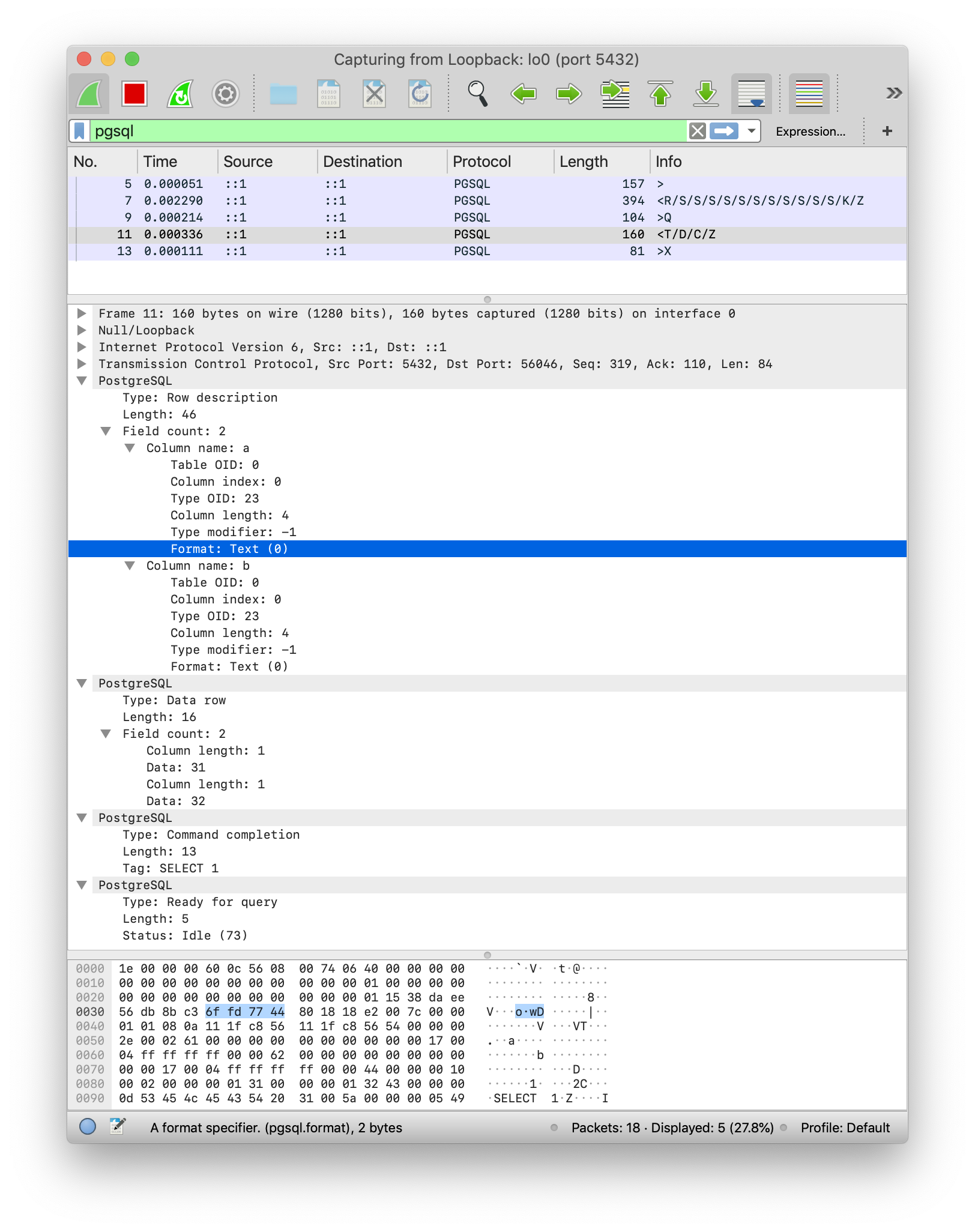
Wireshark内建了对PGSQL的解码,允许我们方便地查看PostgreSQL协议报文的内容。
启动阶段,客户端向服务端发送了一条StartupMessage (F),而服务端回送了一系列消息,包括AuthenticationOK(R), ParameterStatus(S), BackendKeyData(K) , ReadyForQuery(Z)。这里这几条消息都打包在同一个TCP报文中发送给客户端。
简单查询阶段,客户端发送了一条Query (F)消息,将SQL语句SELECT 1 AS a, 2 AS b;直接作为内容发送给服务器。服务器依次返回了RowDescription(T),DataRow(D),CommandComplete(C),ReadyForQuery(Z).
终止阶段,客户端发送了一条Terminate(X)消息,终止连接。
题外话:使用Mac进行无线网络嗅探
结论: Mac: airport, tcpdump Windows: Omnipeek Linux: tcpdump, airmon-ng
以太网里抓包很简单,各种软件一大把,什么Wireshark,Ethereal,Sniffer Pro 一抓一大把。不过如果是无线数据包,就要稍微麻烦一点了。网上找了一堆罗里吧嗦的文章,绕来绕去的,其实抓无线包一条命令就好了。
Windows下因为无线网卡驱动会拒绝进入混杂模式,所以比较蛋疼,一般是用Omnipeek去弄,不细说了。
Linux和Mac就很方便了。只要用tcpdump就可以,一般系统都自带了。最后-i选项的参数填想抓的网络设备名就行。Mac默认的WiFi网卡是en0。 tcpdump -Ine -i en0
主要就是指定-I参数,进入监控模式。 -I :Put the interface in "monitor mode"; this is supported only on IEEE 802.11 Wi-Fi interfaces, and supported only on some operating systems. 进入监控模式之后计算机用于监控的无线网卡就上不了网了,所以可以考虑买个外置无线网卡来抓包,上网抓包两不误。
抓了包能干很多坏事,比如WEP网络抓几个IV包就可以用aircrack破密码,WPA网络抓到一个握手包就能跑字典破无线密码了。如果在同一个网络内,还可以看到各种未加密的流量……什么小黄图啊,隐私照啊之类的……。
假如我已经知道某个手机的MAC地址,那么只要 tcpdump -Ine -i en0 | grep $MAC_ADDRESS 就过滤出该手机相关的WiFi流量。
具体帧的类型详情参看802.11协议,《802.11无线网络权威指南》等。
顺便解释以下混杂模式与监控模式的区别: 混杂(promiscuous)模式是指:接收同一个网络中的所有数据包,无论是不是发给自己的。 监控(monitor)模式是指:接收某个物理信道中所有传输着的数据包。
RFMON RFMON is short for radio frequency monitoring mode and is sometimes also described as monitor mode or raw monitoring mode. In this mode an 802.11 wireless card is in listening mode (“sniffer” mode).
The wireless card does not have to associate to an access point or ad-hoc network but can passively listen to all traffic on the channel it is monitoring. Also, the wireless card does not require the frames to pass CRC checks and forwards all frames (corrupted or not with 802.11 headers) to upper level protocols for processing. This can come in handy when troubleshooting protocol issues and bad hardware.
RFMON/Monitor Mode vs. Promiscuous Mode Promiscuous mode in wired and wireless networks instructs a wired or wireless card to process any traffic regardless of the destination mac address. In wireless networks promiscuous mode requires that the wireless card be associated to an access point or ad-hoc network. While in promiscuous mode a wireless card can transmit and receive but will only captures traffic for the network (SSID) to which it is associated.
RFMON mode is only possible for wireless cards and does not require the wireless card to be associated to a wireless network. While in monitor mode the wireless card can passively monitor traffic of all networks and devices within listening range (SSIDs, stations, access points). In most cases the wireless card is not able to transmit and does not follow the typical 802.11 protocol when receiving traffic (i.e. transmit an 802.11 ACK for received packet).
Both modes have to be supported by the driver of the wired or wireless card.
另外在研究抓包工具时,发现了Mac下有一个很好用的命令行工具airport,可以用来抓包,以及摆弄Macbook的WiFi。 位置在 /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/Current/Resources/airport
可以创建一个符号链接方便使用: sudo ln -s /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/Current/Resources/airport /usr/sbin/airport
常用的命令有: 显示当前网络信息:airport -I 扫描周围无线网络:airport -s 断开当前无线网络:airport -z 强制指定无线信道:airport -c=$CHANNEL
抓无线包,可以指定信道: airport en0 sniff [$CHANNEL] 抓到的包放在/tmp/airportSniffXXXXX.cap,可以用tcpdump, tshark, wireshark等软件来读。
最实用的功能还是扫描周围无线网络。